

For best results, tests should be performed on a Diversified Drawdown Platform™ or a similar flat surface. Drawdowns allow easy evaluation of wettability, opacity, color match, gloss, tack strength, drying weight, dye uniformity, degree of pigment dispersion, and other attributes. Since most coating properties are thickness-dependent, it is imperative that the optimum thickness be determined for each application. The drawdown test is a fundamental laboratory technique which is used to evaluate interactions between flat surfaces (such as film, foil, and paper) and a myriad of inks, coatings, paints, suspensions, adhesives, colloids, powders, etc. Theis (1935) solution for a nonleaky confined aquifer shown by red curve (data from USBR 1995).Note: drawdown is shown at accelerated speed. Use of composite plot to estimate aquifer properties by matching Hantush and Jacob (1955) type-curve solution to drawdown data collected in three fully penetrating observation wells during a constant-rate pumping test in a leaky confined aquifer. At early time, the drawdown data from all three observation wells follow the Theis type curve for a nonleaky confined aquifer (shown in red) subsequent deviation from the Theis curve marks the onset of vertical leakage into the pumped aquifer. Figure 6 shows a composite plot on semi-log axes for a constant-rate pumping test conducted in a leaky confined aquifer ( USBR 1995). The composite plot is valuable for the analysis of pumping tests that depart from the Theis model, too. Use of composite plot to estimate aquifer properties by matching Cooper and Jacob (1946) straight-line solution to drawdown data collected in three fully penetrating observation wells during a constant-rate pumping test in an unconfined aquifer (data from USBR 1995). īy normalizing the distance between observation and pumping wells (t/r²), composite plots show data from fully penetrating observation wells matching the same Theis (1935) type curve or the same Cooper and Jacob (1946) straight line when the aquifer conforms to the Theissian model (Figure 5).

The composite plot, another tool for analyzing data from multiwell pumping tests, displays drawdown as a function of t/r² where t is time since pumping began, and r is radial distance from pumping well. Estimation of aquifer properties by matching Cooper and Jacob (1946) solution to distance-drawdown data collected in three fully penetrating observation wells after 2045 minutes of constant-rate pumping in an unconfined aquifer (data from USBR 1995). A single drawdown measurement per well, each recorded at the same time, is plotted on a distance-drawdown graph.įigure 4 shows the estimation of aquifer properties from distance-drawdown data collected at the end of a constant-rate pumping test in an unconfined aquifer using the Cooper and Jacob (1946) straight-line solution. Distance-Drawdown Analysisĭistance-drawdown plots (drawdown versus radial distance) are used to estimate aquifer properties from pumping tests with more than one observation well. The derivative shown on the plot (crosses) guides the fit of the straight line to drawdown data from the infinite-acting radial flow period (data from Walton 1962). Estimation of aquifer properties by matching Cooper and Jacob (1946) straight-line solution to time-drawdown data (squares) collected in an observation well during a constant-rate pumping test in a nonleaky confined aquifer. Curve matching may be performed using type-curve methods on log-log plots (Figure 2) or straight-line methods on semi-log plots (Figure 3). Typically, aquifer properties are estimated from a constant-rate pumping test by fitting mathematical models to drawdown data through a procedure known as curve matching. Estimation of aquifer properties by matching Theis (1935) type-curve solution to time-drawdown data collected in an observation well during a constant-rate pumping test in a nonleaky confined aquifer (data from Walton 1962). distance-drawdown analysis (s versus r).
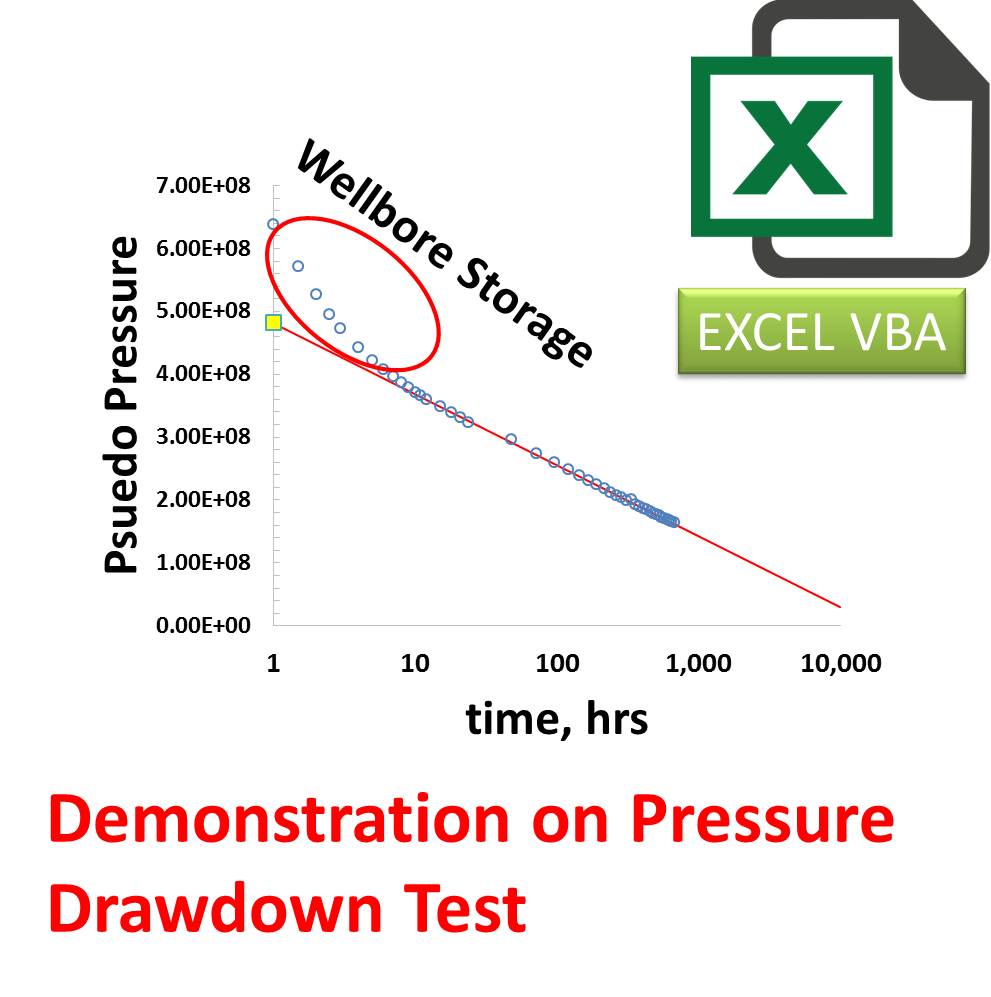
Common methods of interpreting constant-rate pumping tests include the following:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
